Diathermy
Electric currents (radio and sound waves) used to generate heat in layers of your skin below the surface.
Strengthening Exercises
Focused on improving muscle strength in affected limbs.
Gait training
Exercises to improve walking ability, often with assistive devices.
Posture and Mobility Exercises
To improve spinal alignment and movement patterns. Balance and Coordination Training: To reduce falls and improve functional mobility.
Electric muscle stimulation (EMS)
Non-invasive therapy that uses electrical currents to activate muscles.
Myofascial release (MFR)
Massage therapy technique that uses gentle, constant pressure to relieve pain and tightness in the body’s myofascial tissues.
Therapeutic ultrasound
Non-invasive procedure that uses ultrasound waves to treat pain and other conditions.
Infrared light therapy
Non-invasive treatment that uses light to treat pain and inflammation, and to promote healing.
Soft tissue release
Massage technique that can help reduce pain and muscle tension.
Benefits include:
Improved mobility, increased strength and endurance, enhanced balance and coordination, greater independence, and prevention of secondary complications (such as muscle contractures, pressure ulcers and joint stiffness).
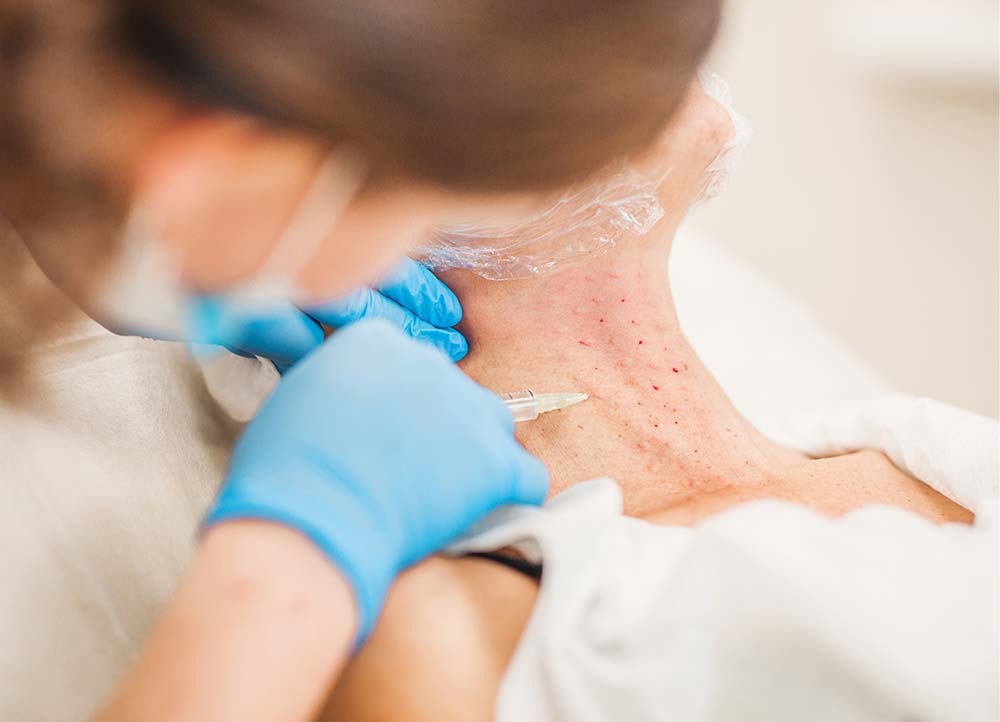
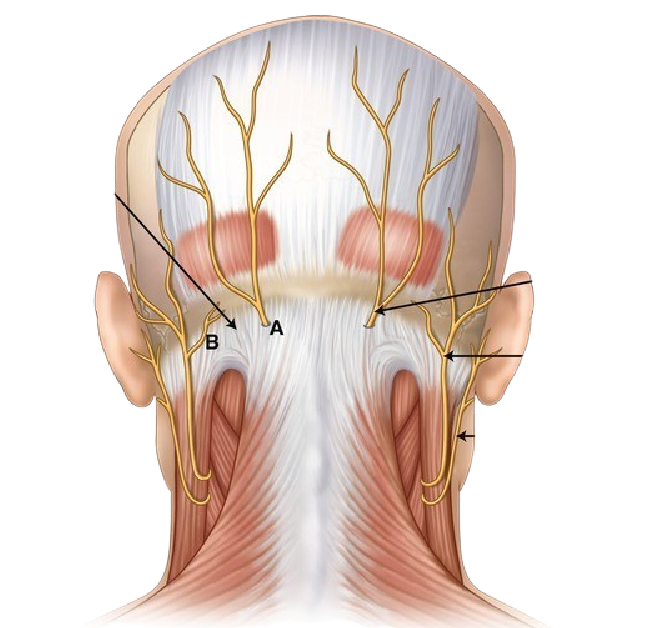
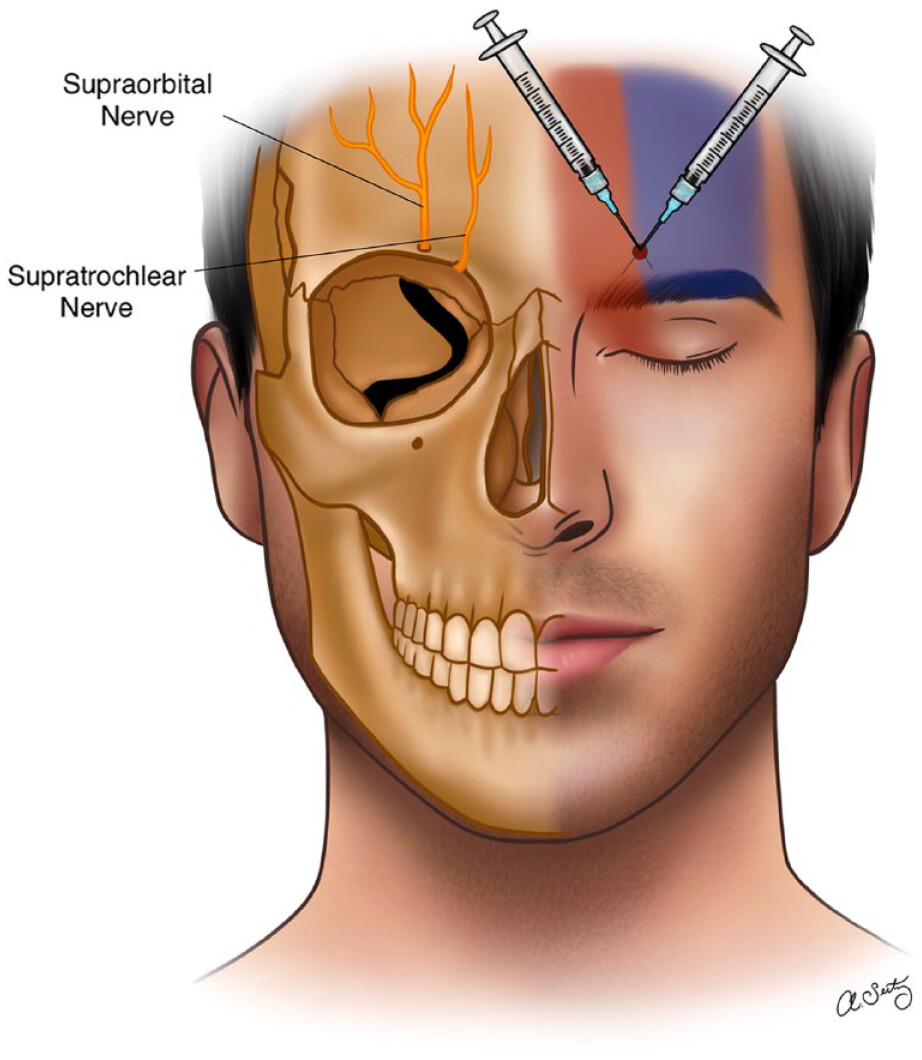
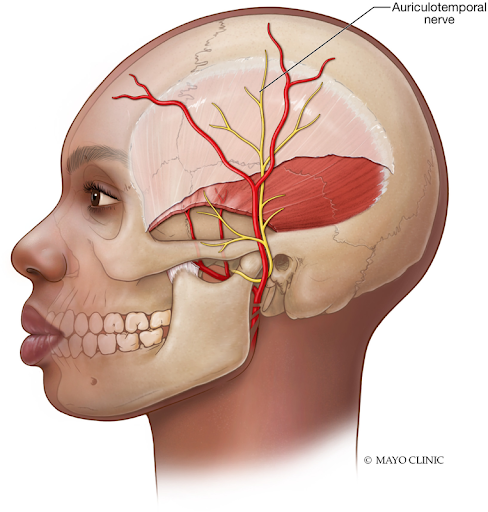
Botox Treatment
Botox injections in the scalp and neck can prevent chronic migraines by blocking pain signals, and has been shown to be effective for chronic migraine prevention. Read more about Botox injections below.
Chronic Migraine
Patients who experience frequent and debilitating migraine attacks that have not responded adequately to other preventive treatments.
Refractory Migraine
Individuals who have tried multiple oral migraine preventive medications without significant relief.
Migraine with Medication Overuse
Patients who overuse acute medications (e.g., triptans, NSAIDs) and have developed a chronic daily headache pattern.
Quality of Life Impact
When migraines significantly impair daily function and quality of life, preventing work, social activities, or other important daily tasks.

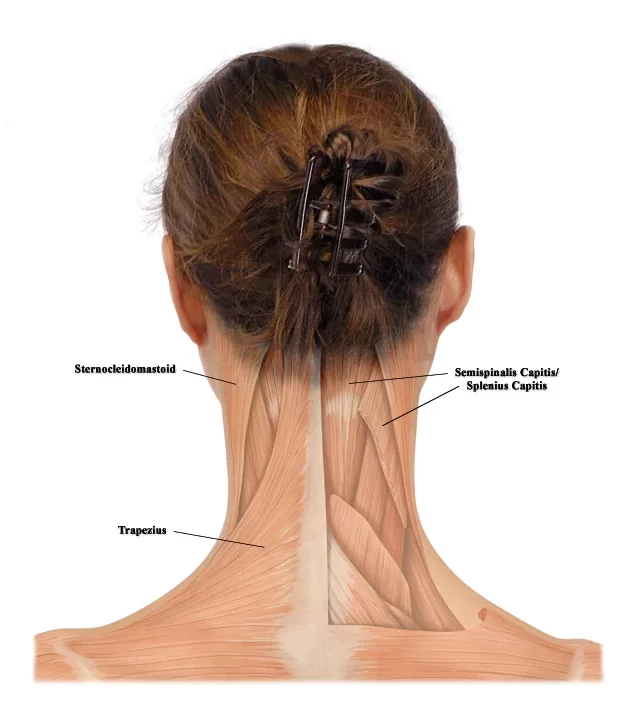
Cervical Dystonia (Spasmodic Torticollis)
Affects the neck muscles and causes abnormal head positioning, pain, and spasms.
Blepharospasm
Involuntary contraction of the muscles around the eyes, causing uncontrollable blinking or closure of the eyelids
Focal Hand Dystonia (e.g., Writer’s Cramp)
Involuntary muscle contractions in the hand or forearm that interfere with writing or other precise hand movements.
Oromandibular Dystonia
Involuntary muscle contractions affecting the jaw, mouth, and face, leading to difficulties in speaking or eating.